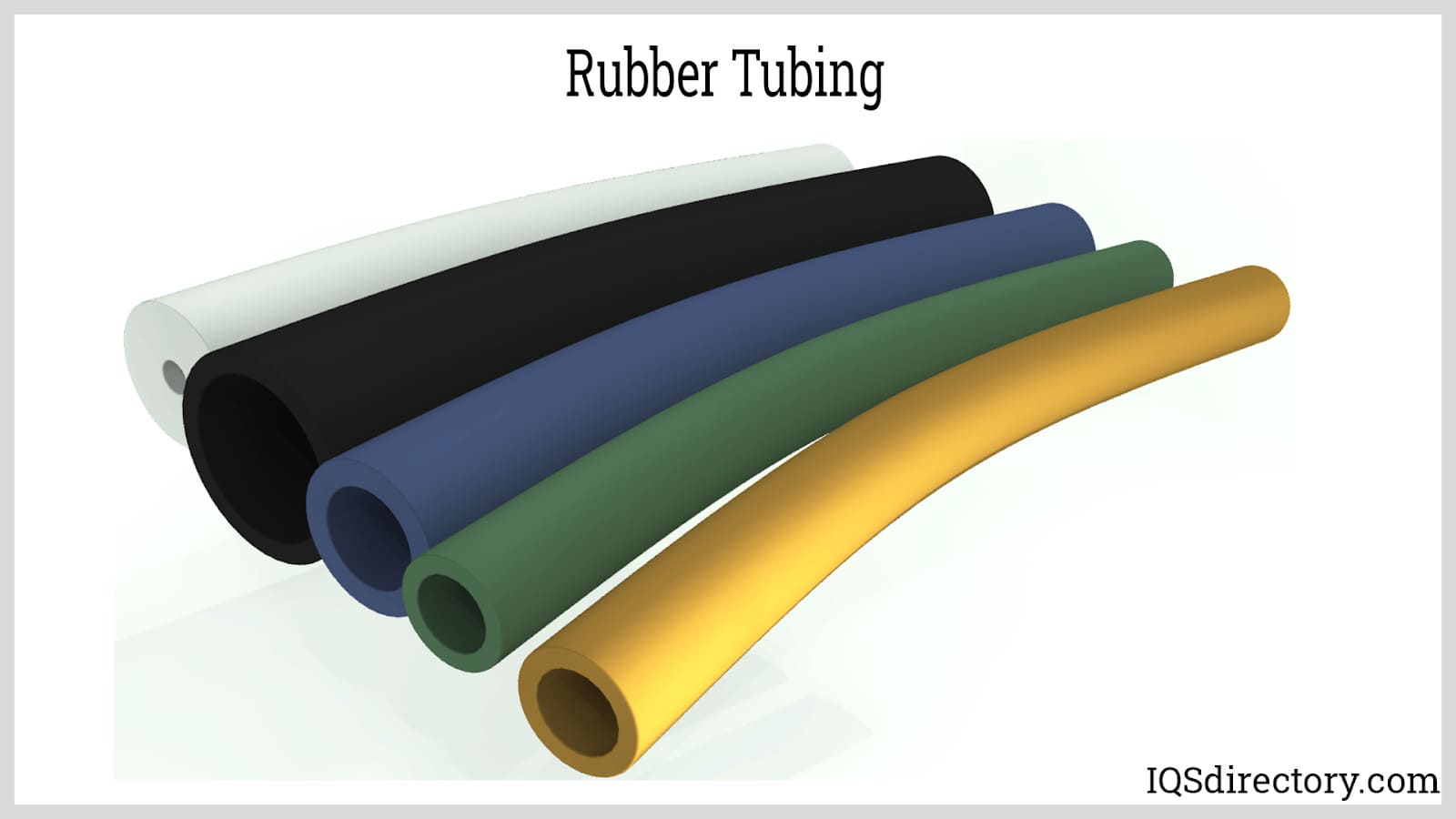
Surgical tubing is frequently made from silicone or latex, and each material has its own benefits and disadvantages. Read More…
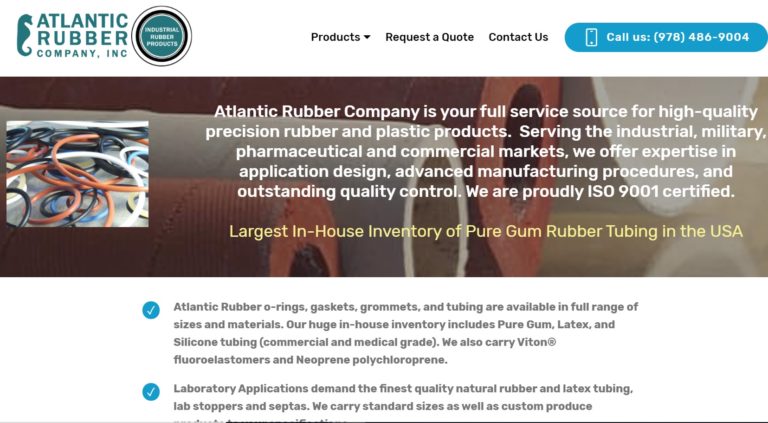
As the largest in-house pure gum inventory carrier in the U.S., Atlantic Rubber Company has cost-effective and resilient rubber tubing. We carry a variety of materials so that we can make the best product for your needs.
At Kent Rubber Supply Co., we specialize in providing high-quality rubber tubing solutions to meet the diverse needs of our customers. With decades of experience in the industry, we take pride in offering a comprehensive selection of durable, reliable, and customizable rubber tubing products. Our tubing is designed to perform in a wide range of applications, including industrial, commercial, and...

National Rubber is your source for extruded, Molded, Die cut & Secondary fabrication work in rubber products, tubing and shapes made out of Silicone, Flurosilicone, Viton, Nitrile, Neoprene, EPDM, SBR,butyl & any custom compound. We offer our customers high quality, complex shapes and fast turn-around times.

Established in 1986, GSH Industries supplies plastic, aluminum and rubber tubing to an array of industries including automotive, consumer, marine and electrical.
More Surgical Tubing Manufacturers
Comprehensive Guide to Silicone and Surgical Tubing: Properties, Uses, and Selection Tips
Silicone is an inert compound, meaning that it is generally non-reactive when brought into contact with other substances. As a result, silicone tubing is highly valued for its chemical resistance and stability in a wide range of medical device and industrial applications. Compared to latex, silicone exhibits a superior deterioration rate, outstanding resistance to extreme temperatures, and excellent elasticity. However, one factor to note is that silicone does not maintain its shape memory as effectively as some other materials—if stretched, it may remain elongated rather than returning to its original length.
Latex tubing offers a different set of benefits. This material is prized for its exceptional stretchiness and strong gripping power. When pulled, twisted, or stretched, latex tubing reliably returns to its original shape, making it ideal for applications that require flexibility and repeated movement. The walls of surgical tubing—often made from latex or silicone—are generally thin, ensuring maximum flow of fluids without the need for a larger tube diameter.
Key Features and Material Properties
When selecting tubing for medical, laboratory, or industrial use, it’s essential to consider the different properties of available materials. Here’s how silicone tubing compares to latex and other common options:
- Chemical Resistance: Silicone is highly resistant to chemicals, solvents, and oils, making it safe for use in medical and pharmaceutical environments where contamination is a concern.
- Temperature Tolerance: Silicone tubing can withstand a wide temperature range, from -100°F to 500°F (-73°C to 260°C), which is ideal for autoclaving, sterilization, and applications involving hot or cold fluids.
- Flexibility and Elasticity: Latex tubing is extremely flexible and can be stretched repeatedly without permanent deformation, while silicone provides moderate elasticity but less shape memory.
- Transparency and Color Options: Both silicone and latex tubing are available in clear or colored varieties, enabling easy visual inspection of fluid flow and compatibility with color-coding systems in hospitals or laboratories.
- Biocompatibility: Medical-grade silicone and latex are both considered biocompatible, but silicone is often preferred for long-term implantable devices due to its inert nature.
- Durability: Silicone generally offers better resistance to UV light, ozone, and aging, while latex may degrade more quickly in harsh environments.
Common Applications and Industries
Surgical tubing is a versatile product critical to many sectors. Understanding the main applications for silicone tubing and surgical tubing can help you determine which product best fits your needs:
- Medical Devices: Used in oxygen delivery, air and fluid transfer, suction tubes, intravenous (IV) lines, catheters, peristaltic pumps, cardiac tubing, and surgical drains.
- Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: Employed in transferring active ingredients, solvents, and finished products due to its compatibility with sterile processes.
- Laboratory Use: Ideal for transferring gases and liquids in analytical and research settings; compatible with laboratory glassware and chemical apparatus.
- Food and Beverage Processing: FDA-approved silicone tubing is used for beverage dispensing, dairy processing, and food handling, thanks to its non-toxic and odorless properties.
- Biotechnology: Supports sterile fluid pathways in bioreactors, fermentation, and cell culture applications.
- Industrial Applications: Used in chemical processing, electronics manufacturing, and fluid handling systems that require high purity and temperature resistance.
- Hobby and Recreational Use: Latex surgical tubing is popular in fishing (jigs and lures), slingshots, exercise equipment, model building, and home DIY projects.
How Do You Choose Between Silicone and Latex Tubing?
When selecting tubing for your specific project or industry, consider these factors:
- Chemical Compatibility: Will the tubing come into contact with aggressive chemicals, solvents, or oils?
- Temperature Requirements: Does your application involve exposure to high or low temperatures, autoclaving, or sterilization?
- Flexibility and Stretch: Do you need tubing that can be stretched, twisted, or repeatedly compressed without permanent deformation?
- Regulatory Compliance: Is FDA, USP Class VI, or other medical or food-grade certification required?
- Transparency: Is visual monitoring of fluid flow important for your application?
- Longevity: Does your system require tubing that resists UV rays, weathering, or aging over time?
Pro Tip: For most medical and laboratory environments where high purity, inertness, and sterilization are essential, silicone tubing is the preferred choice. For applications requiring maximum stretch and gripping power, such as exercise bands or slingshots, latex tubing is often superior.
Types of Tubing and Customization Options
Both silicone and latex tubing are available in a wide variety of sizes, wall thicknesses, and diameters to accommodate different flow rates and pressure requirements. Manufacturers offer customization options to meet unique application needs, such as:
- Inner and Outer Diameter Selection: Precise sizing ensures compatibility with medical connectors, pumps, and laboratory equipment.
- Wall Thickness: Thicker walls provide higher pressure resistance, while thin-walled tubing maximizes fluid flow and flexibility.
- Color Coding: Colored tubing helps differentiate lines in complex systems, supporting safety and workflow efficiency in both clinical and industrial settings.
- Pre-cut Lengths or Continuous Rolls: Choose between standard cut lengths for immediate use or bulk rolls for custom cutting and installation.
- Surface Finish: Smooth or textured finishes can improve grip, reduce kinking, or enhance fluid flow depending on the application.
- Specialty Grades: Medical-grade, food-grade, high-purity, platinum-cured, and peroxide-cured silicone options are available for specialized needs.
Manufacturing and Processing Methods
Natural gum rubber is derived from natural latex, a milky fluid harvested from the Pará rubber tree and other plant species. In contrast, synthetic rubber—including silicone and neoprene—originates from petroleum-based chemicals. The choice of raw materials and additives significantly affects the final product’s characteristics, including:
- Durability: Enhanced by compounding and the use of reinforcing fillers.
- Tensile Strength: Improved through cross-linking and curing processes.
- Temperature and Chemical Resistance: Achieved through careful selection of polymer base and curing agents.
- Coloration: Dyes and pigments are added for identification purposes. Some rubbers accept color more readily, but coloration does not affect tubing performance.
Different manufacturing processes are used to shape tubing:
- Extrusion: Raw rubber or silicone is forced through a die to create continuous tubing of specific diameter and wall thickness. This method is ideal for producing long, uniform tubes used in medical and industrial applications.
- Dipping: Mandrels (long, thin rods) are dipped in liquid rubber or latex, then cured using steam or heat. The tubing is then stripped from the mandrels, resulting in seamless tubes with a smooth internal surface and no weak areas.
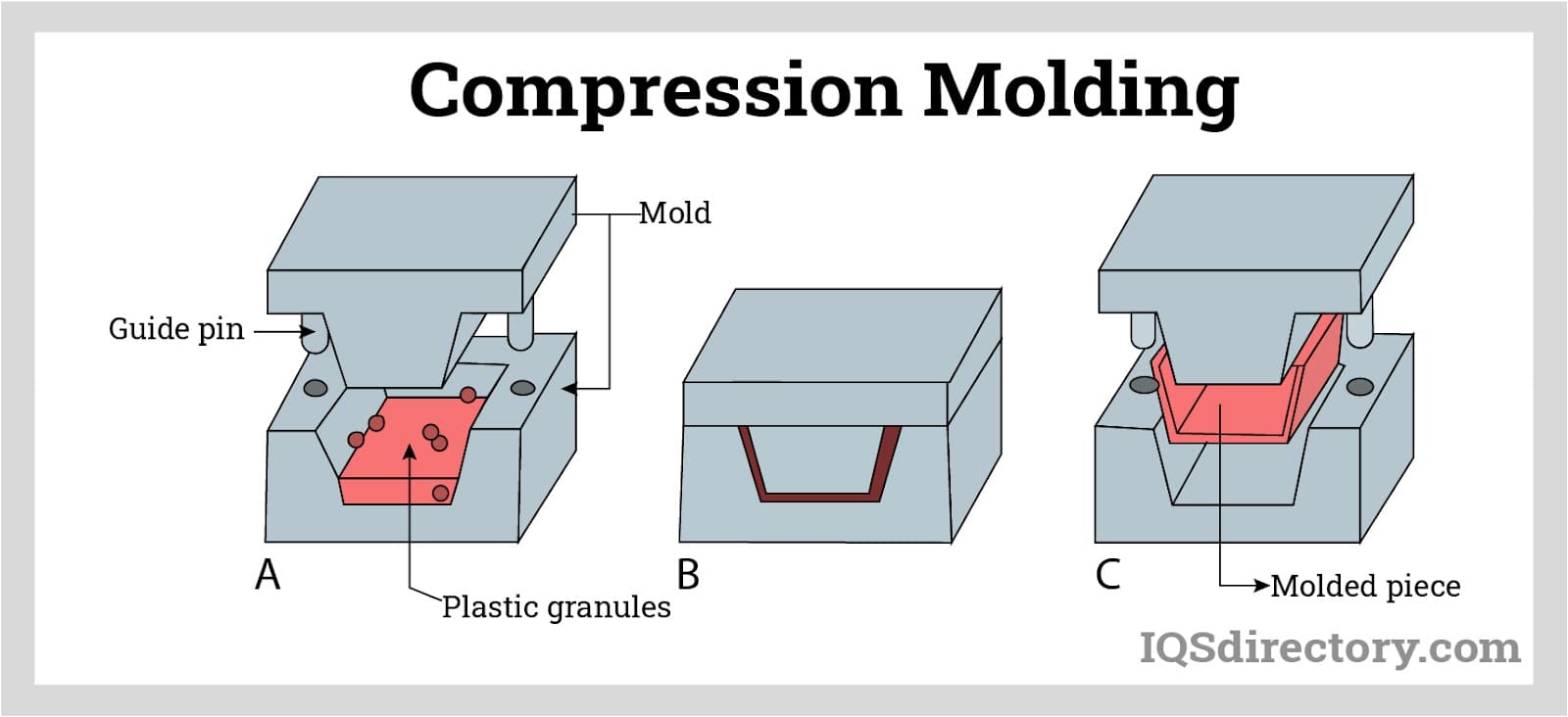
- Molding: Used for custom shapes, connectors, or reinforced tubing sections that require precise geometry.
Sterilization and Clean Room Compatibility
Because surgical tubing is often used in sterile and clean room environments, it must be manufactured, handled, and packaged to avoid contamination. Common sterilization methods include:
- Dry Heat: Used for heat-resistant materials.
- Gamma Radiation: Suitable for sealed, pre-packaged tubing; effective against a wide range of pathogens.
- Chemical Disinfection: Utilized for heat-sensitive materials or when rapid turnaround is needed.
- Autoclaving: High-pressure steam sterilization is commonly applied to silicone tubing and some latex tubing, depending on formulation.
Looking for tubing that meets specific sterilization protocols? Ask us about options for gamma-irradiated, pre-sterilized, or clean room-packaged silicone and latex tubing.
Benefits of Silicone Tubing and Surgical Tubing
Choosing the right tubing for your application delivers significant advantages, particularly in demanding environments. Key benefits include:
- High Purity and Inertness: Silicone tubing does not react with most chemicals or fluids, maintaining sample integrity in pharmaceutical, medical, and food applications.
- Wide Temperature Range: Withstands extreme hot and cold without loss of flexibility or structural integrity.
- Low Extractables: Medical-grade silicone tubing leaches minimal substances, reducing the risk of contamination.
- Ease of Sterilization: Compatible with multiple sterilization methods, supporting compliance with cleanliness standards in regulated industries.
- Long Service Life: Resistant to aging, UV light, ozone, and weathering, ensuring reliable performance over time.
- Softness and Flexibility: Both silicone and latex tubing provide a soft, pliable structure that is comfortable for patient contact and easy to handle during installation.
- Customizability: Available in a wide range of sizes, shapes, and colors to suit specific applications and workflow requirements.
Ready to Find the Perfect Tubing?
Explore our complete range of silicone tubing and surgical tubing solutions designed for medical, laboratory, food processing, and industrial use. Not sure which tubing type is best for your project? Contact our technical support team for expert guidance and personalized recommendations.
Frequently Asked Questions: Surgical and Silicone Tubing
What is surgical tubing made of?
Surgical tubing is typically made from medical-grade silicone rubber or natural latex rubber. The material choice depends on the intended application, with silicone preferred for its chemical resistance, temperature tolerance, and inertness, while latex is favored for its superior elasticity and stretch.
Is silicone tubing safe for food and beverage contact?
Yes, FDA-approved food-grade silicone tubing is widely used in food, beverage, and dairy processing. It is non-toxic, tasteless, odorless, and does not leach harmful substances, making it ideal for transferring consumable products.
Can silicone tubing be autoclaved?
Silicone tubing is highly resistant to heat and can be repeatedly sterilized using an autoclave without losing flexibility or structural integrity. This makes it suitable for applications in hospitals, laboratories, and pharmaceutical manufacturing.
What are the differences between latex and silicone tubing?
- Latex tubing is highly elastic, providing strong grip and return-to-shape properties, but may degrade over time when exposed to UV light or ozone.
- Silicone tubing is less elastic but offers superior chemical resistance, temperature tolerance, and longevity in harsh conditions.
- Both materials are biocompatible, but silicone is often chosen for long-term implantable devices.
How do I determine the right tubing size for my application?
Consider the required flow rate, pressure, and compatibility with connectors or fittings. Review product specifications for inner diameter (ID), outer diameter (OD), and wall thickness. If unsure, consult with a tubing expert to ensure optimal fit and performance.
Can I order customized tubing?
Absolutely. Many manufacturers offer custom extrusion, pre-cut lengths, color-coding, and specialty formulations to meet unique requirements. Contact us to discuss your specific needs and request a quote for custom surgical or silicone tubing.
Use Cases and Industry Examples
- Hospitals and Medical Clinics: Intravenous lines, wound drainage, oxygen delivery, surgical drains, and infusion pumps rely on silicone and latex tubing for safe, sterile fluid management.
- Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: High-purity silicone tubing is used for transferring sensitive ingredients and finished products, ensuring regulatory compliance and product integrity.
- Research Laboratories: Scientists and lab technicians use chemically resistant tubing for transferring reagents, gases, and biological samples in controlled environments.
- Food & Beverage Industry: Silicone tubing is used in beverage dispensing equipment, dairy processing, and food manufacturing lines for its flexibility, purity, and ease of cleaning.
- Electronics Manufacturing: Tubing is utilized in fluid cooling, chemical transfer, and clean room processes where contamination must be minimized.
- Hobbies and Recreation: Latex tubing’s stretch and grip properties make it popular for slingshots, exercise resistance bands, fishing lures, and model airplanes.
How to Buy Surgical and Silicone Tubing: Decision Factors
When researching where to buy silicone or surgical tubing, consider the following checklist to ensure you select a product that matches your application:
- Material Compatibility: Confirm that the tubing material is compatible with all fluids, gases, and chemicals it will contact.
- Size and Fit: Verify inner and outer diameters, wall thickness, and compatibility with connectors or barbed fittings.
- Certification and Compliance: Look for FDA, USP Class VI, ISO 10993, or other relevant certifications for medical and food-grade use.
- Sterility: Determine if pre-sterilized or clean room-packaged tubing is required for your workflow.
- Customization: Explore options for custom colors, cut lengths, or specialty grades for unique applications.
- Supplier Reputation: Choose trusted suppliers with a track record of quality products, technical support, and on-time delivery.
Ready to compare silicone tubing vs. latex tubing for your project? Browse our product catalog or request a sample or technical data sheet today.
Still have questions about choosing the right surgical or silicone tubing for your needs? Contact our technical experts for personalized recommendations, product samples, and a competitive quote. Discover why leading hospitals, laboratories, and manufacturers trust our tubing solutions for performance, purity, and reliability.





 Rubber Extrusions
Rubber Extrusions Rubber Molding
Rubber Molding Rubber to Metal Bonding
Rubber to Metal Bonding Rubber Tubing
Rubber Tubing Vibration Absorbers
Vibration Absorbers Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services